Benefits of Blockchain in Finance: Key Advantages and Impacts

Blockchain technology is shaking up the finance world. If you’re a financial professional, understanding blockchain is no longer optional—it’s essential. This blog will guide you through the benefits and impacts of blockchain in finance, offering clear insights into why this technology is a game-changer.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology in Finance
Brief Overview of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures that each transaction is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, making it both innovative and resilient.
Importance of Blockchain in Modern Finance
Blockchain’s importance in modern finance cannot be overstated. It promises a future where transactions are faster, more secure, and more transparent. Financial professionals who grasp blockchain’s potential can unlock (don’t use this word) new opportunities for innovation and efficiency in their organizations.
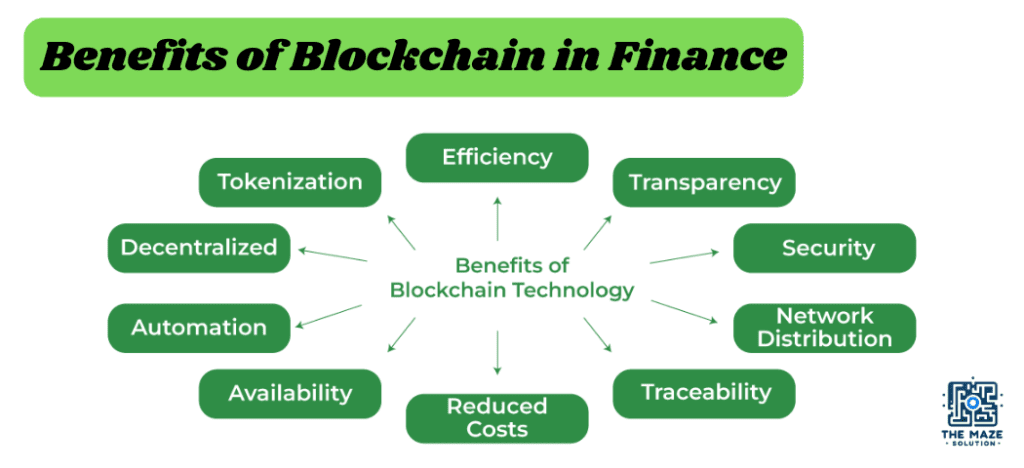
Understanding the Benefits of Blockchain in Finance
Definition and Key Features
Blockchain is defined by three main features:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain.
- Transparency: All participants have access to the same data.
- Security: Transactions are secured through cryptographic methods.
General Benefits of Blockchain in Finance
Enhanced Security and Fraud Reduction
Blockchain’s cryptographic security measures make it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to alter transaction data. This significantly reduces fraud and enhances trust among participants.
Improved Transparency and Traceability
Every transaction on a blockchain is recorded and visible to all network participants. This transparency ensures that all actions are traceable, which is crucial for auditing and compliance.
Faster Transactions and Settlement Times
Traditional financial systems often require multiple intermediaries, slowing down transaction times. Blockchain eliminates these intermediaries, allowing for near-instantaneous transactions and settlements.
Advantages of Blockchain in Financial Services
Improved Payment Processing
Instant Cross-Border Transactions
Blockchain enables real-time cross-border payments. Unlike traditional banking systems that can take days, blockchain transactions are processed in minutes, regardless of geography.
Reduced Transaction Fees
By cutting out intermediaries, blockchain reduces the costs associated with transaction fees. This is especially beneficial for international payments, which are typically expensive.
Efficient Identity Verification
Streamlined KYC (Know Your Customer) Processes
Blockchain simplifies the KYC process by storing verified customer identities on a secure, immutable ledger. This reduces the time and cost associated with KYC compliance.
Reduced Risk of Identity Theft
Storing identity information on a blockchain reduces the risk of identity theft. The cryptographic security ensures that only authorized parties can access sensitive information.
Smart Contracts
Automation and Enforcement of Contracts
Smart contracts represent a revolutionary development in the field of digital transactions and agreements. Essentially, these are self-executing contracts where the terms and conditions are directly written into lines of code. This code is stored and replicated on the blockchain, ensuring that the contract is both transparent and immutable.
The primary advantage of smart contracts is their ability to automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement without the need for human intervention. Here’s how they work:
- Code as Law: The conditions of the contract are predefined and coded into the blockchain. For example, a smart contract for a rental agreement might include terms such as rental amount, due date, and conditions for payment.
- Automated Execution: Once the predefined conditions are met, the smart contract automatically executes the agreed-upon actions. For instance, if the tenant pays the rent on time, the smart contract might automatically transfer the payment to the landlord and generate a receipt.
- Self-Enforcement: The execution of the contract is governed by the blockchain’s consensus mechanism. This ensures that the contract cannot be tampered with or altered once it is deployed. The automated enforcement reduces the risk of non-compliance and ensures that both parties adhere to the agreed terms.
This automation significantly reduces the need for intermediaries such as lawyers, notaries, or escrow services, who are typically involved in the enforcement and execution of traditional contracts. As a result, smart contracts can lead to substantial savings in time and legal fees.
Reduction in Intermediaries and Costs
Smart contracts’ ability to automate the execution of agreements directly leads to a reduction in the need for third-party intermediaries. This has several important implications:
Transparency and Trust: Smart contracts operate on transparent blockchain networks where all parties can verify the terms and conditions of the contract. This transparency builds trust among participants, as everyone has access to the same information and can be assured that the contract will be executed as agreed.
Cost Reduction: Traditional contracts often require intermediaries to facilitate, verify, and enforce the terms of an agreement. These intermediaries charge fees for their services, which can add up to a significant cost. Smart contracts eliminate the need for these intermediaries by automating the process, thereby reducing overall transaction costs.
Increased Efficiency: By removing intermediaries, smart contracts streamline the entire process of contract execution. Transactions can be completed faster because there is no need to wait for third-party approvals or manual processing. This increased efficiency can be particularly beneficial in industries where time is of the essence, such as finance, real estate, and supply chain management.
Enhanced Security: The decentralized nature of blockchain technology ensures that smart contracts are secure and tamper-proof. Since the contract is stored on a distributed ledger, it is resistant to hacking and fraud. This level of security further reduces the need for intermediaries who traditionally provide a layer of trust and verification.
Blockchain Benefits for the Financial Industry
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Cryptographic Security Measures
Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. This makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to breach the system, ensuring high levels of data security and privacy.
Prevention of Data Breaches
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it more resilient to attacks. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network remains secure, preventing large-scale data breaches.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Reduction in Administrative and Operational Costs
Blockchain technology streamlines various administrative processes, reducing the need for manual intervention. This leads to significant cost savings in administrative and operational tasks.
Simplified Reconciliation Processes
Blockchain technology provides a single version of the truth, making reconciliation processes more straightforward. Multiple parties can access and verify data in real-time, reducing discrepancies and errors.
Financial Inclusion
Access to Banking Services for the Unbanked Population
Blockchain technology has the potential to bring financial services to the unbanked population. By eliminating the need for traditional banking infrastructure, blockchain can provide secure and accessible financial services to underserved communities.
Empowerment of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Blockchain technology offers SMEs access to transparent and efficient financial services. This can include supply chain financing, payment processing, and even access to global markets, empowering them to compete with larger enterprises.
Blockchain Technology in Banking Advantages
Revolutionizing Traditional Banking
Streamlined Back-Office Operations
Blockchain can automate many back-office operations, such as clearing and settlement. This reduces the time and cost associated with these processes, making banks more efficient.
Reduced Risk of Fraud and Errors
Blockchain’s secure and transparent nature reduces the risk of fraud and errors in banking operations. Every transaction is recorded and immutable, providing a reliable audit trail.
Innovations in Banking Services
Blockchain-Based Lending and Borrowing
Blockchain enables new forms of lending and borrowing through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. These platforms use smart contracts to automate lending processes, reducing the need for traditional banking intermediaries.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms
DeFi platforms offer a range of financial services, from lending and borrowing to trading and insurance, all without the need for traditional financial institutions. This opens up new opportunities for innovation in banking.
Asset Tokenization
Tokenization of Real-World Assets
Blockchain allows for the tokenization of real-world assets, such as real estate or commodities. These tokens can be traded on blockchain platforms, increasing liquidity and accessibility.
Improved Liquidity and Market Access
Tokenization improves liquidity by making it easier to buy and sell fractional ownership of assets. This democratizes access to investment opportunities, allowing more people to participate in financial markets.
Blockchain Impact on Finance
Transformative Effects on Financial Markets
Enhanced Transparency and Trust in Financial Markets
Blockchain technology revolutionizes financial markets by significantly enhancing transparency. The core feature of blockchain is its immutable ledger, which records every transaction in a clear and unalterable manner. This means that once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted.
This immutability builds a robust level of trust among market participants and regulators. Investors can be assured that the records they are viewing are accurate and untampered with, leading to increased confidence in the market. Regulators also benefit from this transparency, as they can monitor transactions in real-time, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring market integrity.
Real-Time Auditability and Compliance
The transparency of Blockchain technology also facilitates real-time auditability and compliance. In traditional financial systems, auditing is a cumbersome process that often involves extensive paperwork and delayed reporting. Blockchain, however, provides a seamless and immediate access to transaction data, allowing auditors and regulators to verify transactions as they happen.
This capability ensures that all parties adhere to legal and regulatory requirements without the lag time associated with conventional methods. For instance, financial institutions can automatically report transactions to regulatory bodies, ensuring compliance and reducing the likelihood of errors or fraudulent activities.
Disruption of Traditional Financial Models
Challenges to Traditional Banking Systems
Blockchain technology poses significant challenges to traditional banking systems. Conventional banks are often characterized by slow processing times, high transaction fees, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain addresses these issues by offering faster, cheaper, and more transparent alternatives.
For example, cross-border transactions, which typically take several days to process through traditional banks, can be completed within minutes on a blockchain network. Additionally, the costs associated with these transactions are considerably lower, as blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries. This efficiency forces traditional banks to innovate and adapt to maintain their relevance and competitiveness.
Emergence of New Financial Products and Services
Blockchain technology not only disrupts existing models but also paves the way for new financial products and services. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are one such innovation, allowing users to trade assets directly with one another without the need for a central authority. This reduces the risk of hacking and fraud associated with centralized exchanges.
Stablecoins are another product born from blockchain technology. These digital currencies are pegged to stable assets like the US dollar, providing a reliable medium of exchange that combines the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability of traditional currencies. These innovations offer new ways to trade, invest, and manage assets, opening up a world of possibilities for investors and consumers alike.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Examples of Successful Blockchain Implementations in Finance
Several financial institutions have successfully implemented blockchain technology. For example, JP Morgan’s Quorum blockchain is used for interbank transfers, while IBM’s World Wire facilitates cross-border payments.
Analysis of Their Impact on the Financial Sector
These implementations have shown significant improvements in efficiency, transparency, and security. They demonstrate the transformative potential of blockchain in the financial sector.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits for finance, including enhanced security, increased transparency, and improved efficiency. It has the potential to revolutionize traditional banking and financial services, making them more accessible and inclusive.
Future Outlook
The future of blockchain in finance is bright. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications and improvements. Financial professionals who stay ahead of these trends will be well-positioned to take advantage of the opportunities Blockchain technology offers.
Engage with the Audience
If you’re keen to explore the benefits of blockchain in finance further, consider signing up for our newsletter. Stay updated with the latest trends and insights, and join a community of forward-thinking financial professionals.