Virtual Reality in Architecture: Applications, Benefits, and Its Future Impact on the Industry
Introduction to Virtual Reality in Architecture
Overview of Virtual Reality in Architecture
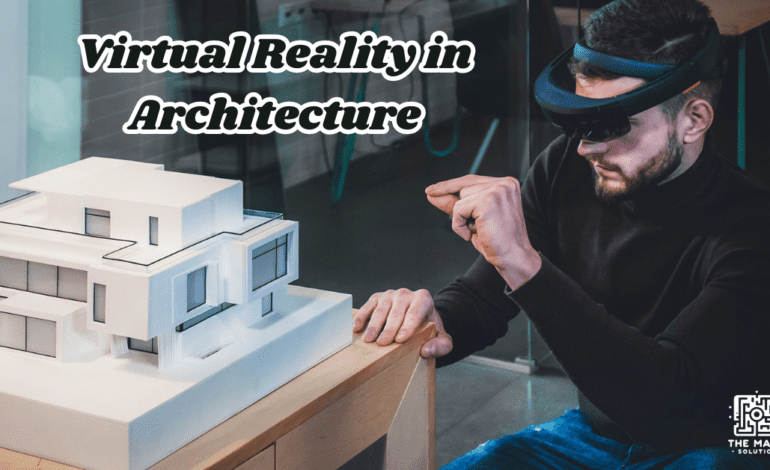
Virtual Reality (VR) in architecture is not just a tech enthusiast’s dream—it’s a groundbreaking development reshaping how architects, clients, and builders interact with design. From its humble beginnings as a concept in science fiction, VR has evolved into a practical tool that offers an immersive experience, allowing users to “walk through” buildings before they are constructed. This innovation is particularly crucial in architecture, where visualizing spatial relationships and design details can make or break a project.
What is VR in Architecture?
Virtual Reality (VR) in architecture represents a significant technological advancement that allows architects, engineers, and clients to immerse themselves in a digital representation of a building or space. By utilizing VR, professionals in the architectural field can create highly detailed and interactive 3D simulations of their designs, enabling users to explore these environments as though they were physically inside the space.
How VR Works in Architecture
At its core, VR in architecture leverages advanced hardware and software to bring architectural designs to life. Here’s a breakdown of how this process works:
- 3D Modeling and Rendering:
- The foundation of VR in architecture lies in creating detailed 3D models of buildings. Architects use specialized software to construct these models, which include every aspect of the design, from structural elements to interior details.
- Once the model is complete, rendering software generates realistic images and simulations. These renderings can include textures, lighting, and even environmental effects, making the virtual space as lifelike as possible.
- Immersive Experiences with VR Headsets:
- To fully experience the architectural design, users wear VR headsets, such as the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. These headsets provide a stereoscopic view, creating a sense of depth and scale that closely mimics real-world vision.
- The headset tracks the user’s head movements, allowing them to look around the virtual environment naturally. This interaction makes it possible to walk through spaces, look up at ceilings, or peer out of windows, just as one would in a physical building.
- Interactive Exploration:
- Beyond just visualizing the space, VR in architecture often includes interactive elements. Users can open doors, move furniture, or even alter the design in real-time. This interactivity is crucial for understanding how a space will function and for making adjustments before construction begins.
- Some VR setups also allow multiple users to explore the environment simultaneously, making it a collaborative tool where architects, engineers, and clients can discuss the design together in real-time.
- Technological Backbone:
- The success of VR in architecture is driven by several key technologies:
- Graphic Processors (GPUs): High-powered GPUs are essential for rendering detailed and complex 3D environments smoothly. They ensure that the virtual experience is free from lag or glitches, which could disrupt the immersion.
- High-Resolution Displays: VR headsets use high-resolution screens to display the virtual environment. The clarity and detail of these displays are critical for making the virtual space feel real and for allowing users to perceive minute details in the design.
- Software Applications: Specialized software like Autodesk Revit, Unity, or Unreal Engine are commonly used in VR architecture. These applications enable the creation and manipulation of 3D models, allowing architects to refine their designs with incredible precision.
- The success of VR in architecture is driven by several key technologies:
Benefits and Impact of VR in Architecture
The introduction of VR in architecture has transformed how professionals approach the design and planning process. It bridges the gap between imagination and reality, providing a tool that enhances visualization, improves client communication, and allows for more innovative design exploration.
Cost and Time Efficiency: By identifying potential issues early in the design phase through VR simulations, architects can avoid costly revisions later. This proactive approach saves time and resources, ensuring that the project stays on schedule and within budget.
Enhanced Visualization: One of the most significant advantages of VR in architecture is its ability to convey the scale and feel of a space in a way that traditional drawings or even 3D models on a screen cannot. Clients can experience the building before it’s built, making it easier to understand the architect’s vision.
Improved Collaboration: VR facilitates better collaboration between architects, engineers, and clients by providing a shared experience where everyone can see and interact with the design simultaneously. This can lead to more informed decisions and fewer changes during the construction phase.
How VR is Integrated into Architectural Processes
The integration of VR in architecture occurs at various stages of the design process. From initial conceptual designs to final walkthroughs, VR provides stakeholders with a comprehensive view of the project, facilitating better decision-making. Examples abound, such as the use of VR to simulate lighting effects and material finishes or to assess the impact of a structure on its surroundings. These applications reveal the growing importance of VR as a tool for enhancing architectural visualization.
Applications of VR in Architecture
Design and Modeling
Architects leverage VR for precise design and modeling, transforming traditional blueprints into dynamic, 3D environments. By donning a VR headset, designers can manipulate models in real-time, adjust dimensions, and experiment with materials—all within a lifelike digital space. This capability ensures that the design intent is accurately represented, reducing the likelihood of costly revisions later.
Client Presentations and Feedback
Virtual reality revolutionizes client presentations by offering immersive experiences that static images or videos cannot match. Clients can explore the proposed space, providing immediate feedback and suggestions. This interactive process fosters collaboration and helps architects align closely with client expectations, ultimately leading to a more satisfied customer base.
Training and Education
In the realm of education, VR serves as a powerful tool for training future architects. Students can engage with complex structures and design principles in a virtual setting, bridging the gap between theory and practice. This hands-on learning approach enhances understanding and prepares students for real-world applications.
Urban Planning and Landscape Design
Urban planners and landscape architects are also tapping into VR’s potential. By simulating entire neighborhoods or parklands, VR aids in assessing the environmental and social impacts of new developments. Real-world examples, such as VR simulations for flood-prone areas, highlight how this technology can inform sustainable urban design practices.
Benefits of VR in Architecture
Enhanced Visualization and Accuracy
One of the most significant benefits of VR in architecture is its ability to enhance visualization. By providing a 360-degree view of a project, VR allows for a more thorough examination of design elements and spatial relationships. This comprehensive perspective leads to greater design accuracy, minimizing errors and ensuring that the final product meets the architect’s vision.
Improved Client Communication
Effective communication is critical in architecture, and VR facilitates this by providing a common visual language. Clients can ‘walk’ through their projects, fostering clearer discussions about design choices. This engagement increases client satisfaction and reduces the risk of misunderstandings.
Cost and Time Efficiency
VR can significantly reduce both project costs and timelines. By identifying potential design flaws early in the process, architects can avoid expensive modifications. Additionally, VR expedites the approval process by providing stakeholders with a detailed understanding of the project, speeding up decision-making.
Innovative Design Exploration
Virtual reality opens the door to innovative design exploration. Architects can experiment with unconventional forms and layouts without the constraints of physical models. This freedom encourages creativity, allowing designers to push the boundaries of what’s possible in architecture.
Impacts of VR in Architecture
Impact on the Design Process
VR is transforming design workflows by making them more interactive and collaborative. Teams can work together in a virtual space, irrespective of geographical location, improving efficiency and fostering innovation. This shift is particularly beneficial in complex projects where coordination is key.
Changes in Client Expectations
As VR becomes more commonplace, client expectations are evolving. Clients now anticipate a more immersive experience in the design phase, which sets higher benchmarks for architectural firms. Those who adapt to this expectation will likely see a competitive advantage.
Influence on the Architectural Industry
The broader architectural industry is feeling the influence of VR through increased competition and innovation. Firms that incorporate VR into their processes are often seen as leaders, attracting top talent and prestigious projects. This trend underscores VR’s role as a differentiator in the industry.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
The rise of VR in architecture also brings ethical and legal considerations. Issues such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure equitable access and fair use of VR technologies.
The Future of VR in Architecture
Emerging Trends in VR for Architecture
The future of VR in architecture is bright, with several emerging trends set to shape the industry. These include the integration of artificial intelligence to automate design processes, the use of augmented reality (AR) to blend digital and physical environments, and the development of more intuitive VR interfaces that enhance user experience.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Despite its promise, VR faces challenges such as high implementation costs and the need for technical expertise. Solutions to these barriers include developing more affordable VR solutions and investing in training programs to build the necessary skills within architectural teams.
Predictions for the Future Impact of VR on Architecture
Experts predict that VR will become an integral part of architectural practice, influencing everything from design to construction. Its potential to revolutionize the industry is immense, offering opportunities for more sustainable, efficient, and innovative architectural solutions.
Conclusion
Recap of the Applications, Benefits, and Impacts of VR in Architecture
In summary, VR in architecture offers numerous applications and benefits, from enhanced visualization and improved client communication to innovative design exploration and cost efficiencies. Its impact on the industry is profound, reshaping how architects design, communicate, and execute projects.
Final Thoughts on the Future of VR in Architecture
The future of VR in architecture is one of limitless possibilities. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises to drive the industry forward, enabling architects to create more dynamic, responsive, and sustainable environments. For those eager to stay at the forefront of architectural innovation, now is the time to explore and integrate VR into your practice.
References
Key Resources on VR in Architecture
For further exploration of Virtual Reality in architecture, consider reviewing resources such as “The VR Book” by Jason Jerald and the journal “Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments,” which offer in-depth insights into the applications and implications of VR technology in the architectural field.